Are you drowsy during the day with no explanation? Do you snore loudly or wake up breathless in the middle of the night? If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, you may be one of more than twelve-million Americans who are affected by sleep apnea.
What is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a condition in which your breathing stops periodically during sleep, as many as 20-30 times per hour. Each time you stop breathing in your sleep, the resulting lack of oxygen alerts your brain, which temporarily wakes you up to restart proper breathing. Since the time spent awake is so brief, most people with sleep apnea don’t remember it, and many feel like they are getting a good night’s sleep, when in fact, they are not. The constant wake-sleep, wake-sleep cycle prevents those with sleep apnea from achieving deep sleep, resulting in a constant drowsy feeling during the day.
What are the signs of sleep apnea?
The following symptoms can indicate the presence of sleep apnea. If you notice one or more of these, contact our practice.
- Insomnia or difficulty sleeping
- Loud snoring at night
- Waking up at night short of breath
- Snorting or choking sounds during the night (indicating a restart of breathing)
- Headaches upon waking in the morning
- Falling asleep unintentionally during the day
- Extreme drowsiness throughout the day
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
The most common type of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea. It occurs due to a physical blockage, usually the collapsing of the soft tissue in the back of the throat. Another form of sleep apnea is central sleep apnea (CSA), in which the breathing stops because the muscles involved don’t receive the proper signal from the brain but this is less common.
What are risk factors for sleep apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea is more common in males than females, and more common in older adults (40+) than younger adults and children. However, anyone — regardless of gender or age — can suffer from sleep apnea. Other risk factors include obesity, smoking, drinking, use of sedatives or tranquilizers, and family history. Central sleep apnea strikes most often in people with heart disorders, neuromuscular disorders, strokes, or brain tumors. It is also more common in males.
Is sleep apnea dangerous?
Sleep apnea is considered a serious medical problem and if left untreated can lead to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart failure and stroke. The ongoing state of fatigue caused by sleep apnea can lead to problems at work or school, as well as danger when driving or operating heavy machinery. Sleep apnea can also cause complications with medication or surgery; sedation by anesthesia can be risky, as can lying flat in bed after an operation. If you know or suspect you suffer from sleep apnea, let your family doctor know before taking prescribed medication or having surgery.
How is obstructive sleep apnea treated?
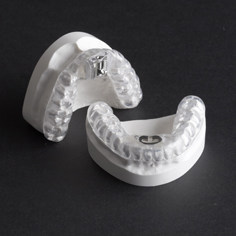
The first line of treatment in obstructive sleep apnea is an oral appliance. This small plastic device fits in the mouth during sleep like a sports mouth guard or orthodontic retainer. Oral appliances help prevent the collapse of the tongue and soft tissues in the back of the throat, keeping the airway open during sleep and promoting adequate air intake. Patients report that an oral appliance is much more preferable to the CPAP that is typically recommended. Oral appliances may be used alone or in combination with other treatments for sleep-related breathing disorders, such as weight management, surgery or CPAP. In cases where the patient has severe obstructive sleep apnea it is typically preferable to go straight to a CPAP.
This is an example of a typical oral appliance:
What should I do if I suspect that someone in my family suffers from sleep apnea?
If you already have a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea, call and schedule a free consult and we will determine if we think that an oral appliance would be the right treatment choice for you. If you haven’t had a diagnosis made then we can refer you to the proper sleep specialist to determine what and to what extent the problem is.

